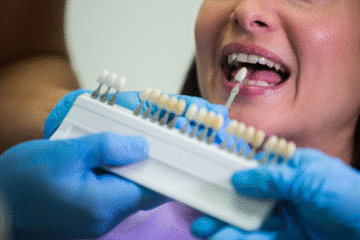
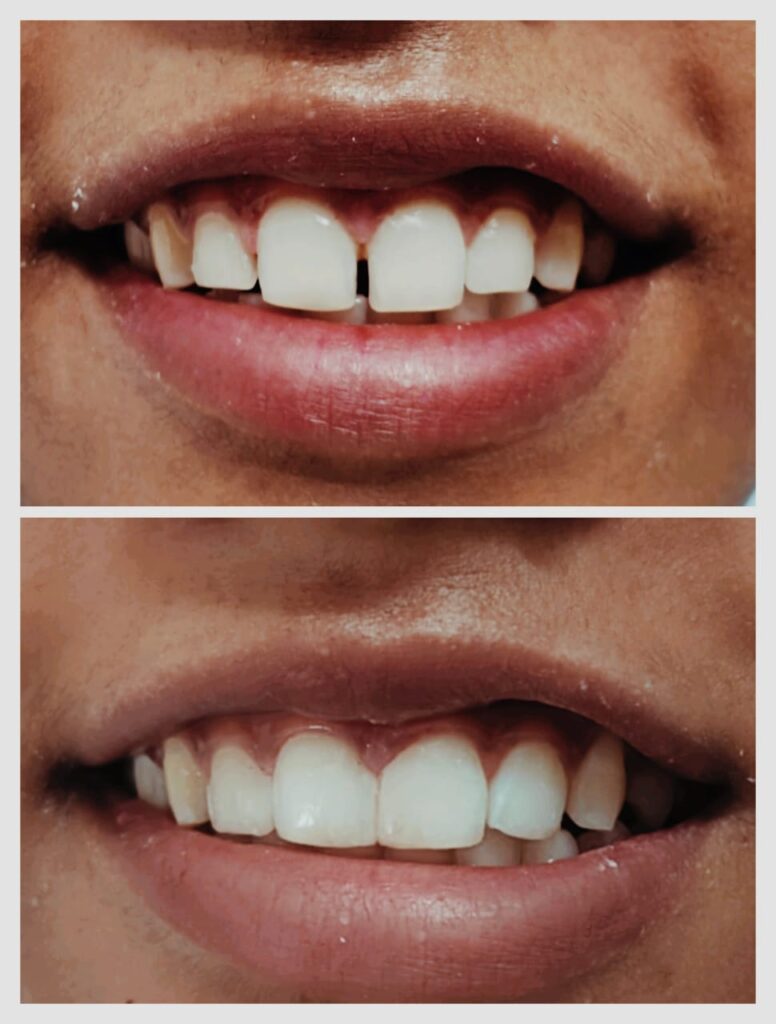
Dental veneers are a popular cosmetic dentistry solution for achieving a radiant and confident smile. These thin, custom-made shells can correct various dental imperfections, enhancing the appearance and functionality of your teeth.
Types of Dental Veneers:
1. Porcelain Veneers: More durable and resistant to stains, porcelain veneers are a popular choice for long-term results.
2. Composite Resin Veneers: Less expensive and requiring less enamel removal, composite resin veneers are ideal for minor corrections.
3. Lumineers: Ultra-thin, no-prep veneers suitable for small teeth or minimal corrections.
4. E.max Veneers: High-strength, glass-ceramic veneers offering exceptional durability and aesthetics.
Procedure:
1. Consultation: Discuss treatment goals and options with your dentist., Initial scan or impression for mock up
2. Trial: Demonstration of how the mock up and final look.
3. Preparation: Shape and prepare the tooth for the veneers and impressions taken.
4. 3. Temporary Veneers: Wear temporary veneers while permanent ones are crafted.
5. 4. Bonding: Permanent veneers bonded to teeth.
Aftercare and Maintenance:
1. Regular Brushing and Flossing: Maintain good oral hygiene.
2. Avoid Hard or Sticky Foods: Prevent chipping or cracking.
3. Regular Dental Check-Ups: Monitor veneer condition.
Potential Risks and Complications:
1. Sensitivity: Temporary sensitivity during bonding process.
2. Chipping or Cracking: Rare, but possible.
3. Gum Recession: Improper placement or gum disease.
4.Decay around the borders of veneer due to poor oral hygiene.
Advantages of Dental Veneers:
1. Improved Smile Aesthetics: Corrects discoloration, gaps, chips, and misshapen teeth.
2. Boosts Confidence: Enhance your self-esteem with a radiant, healthy-looking smile.
3. Durable: Long-lasting results with proper care (10-20 years).
4. Stain-Resistant: Porcelain veneers resist coffee, tea, and wine stains.
5. Minimally Invasive: Conservative preparation preserves natural tooth structure.
Disadvantages of Veneers
1.Irreversible ( due to tooth preparation)
2.Expensive and insurance is not available for cosmetic procedures.
3.Chipping and cracking. Rare but possible
Alternatives to Veneer
1. Teeth Whitening
2. Dental Crowns
3. Orthodontic Treatment
4. Dental Implants
Average Lifespan of Veneers:
1. Porcelain Veneers: 10-20 years.
2. Composite Resin Veneers: 5-10 years.
3. Ceramic Veneers: 10-20 years.
4. Lumineers: 10-20 years.
Factors Affecting Veneer Longevity:
1. Wear and tear
2. Gum recession
3. Tooth decay
4. Chipping or cracking
5. Staining or discoloration
What are the signs of Veneer Wear:
1. Chips or cracks
2. Discoloration or staining
3. Loose or detached veneers
4. Sensitivity or pain
5. Gum recession
Maintenance and Repair:
1. Regular dental check-ups
2. Professional cleanings
3. Repair or replacement of damaged veneers
4. Refinishing or polishing
Extending Veneer Lifespan:
1. Practice good oral hygiene
2. Avoid hard or sticky foods
3. Wear a mouthguard (if grinding or clenching)
4. Schedule regular dental check-ups
5. Consider veneer refinishing or polishing
Replacement Options:
1. New veneers
2. Dental bonding
3. Crowns
4. Implants
Consult your dentist for personalized advice on veneer care and maintenance.