Paediatric Dentistry
Paediatric dentistry is an age-defined specialty that provides both primary and comprehensive preventive and therapeutic oral health care for infants and children through adolescence, including those with special health care needs. Pedodontists are dentists who are specially dedicated for the oral health of children from their infancy through their teen years. You can find us by searching for the best dentist for kids in Indiranagar to ensure expert care for your child’s dental health.
Importance of Milk Teeth
Milk teeth, also known as primary teeth, are the first set of teeth that erupt in a child’s mouth. There are 20 milk teeth in total and they typically erupt from 6 months – 24 months. They play a vital role in a child’s oral health and development. Here are some reasons why milk teeth are important:
Common Oral Disease in Children and its Management
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay in children is a matter of concern. They are prone to such decay mostly due to poor oral hygiene habits. And it’s self explanatory about the affinity of a child to consuming sugary or acidic foods or drinks. Both combined together lead to initiation and progression of decays. The other factors which contribute to this include inadequate fluoride exposure and genetics.
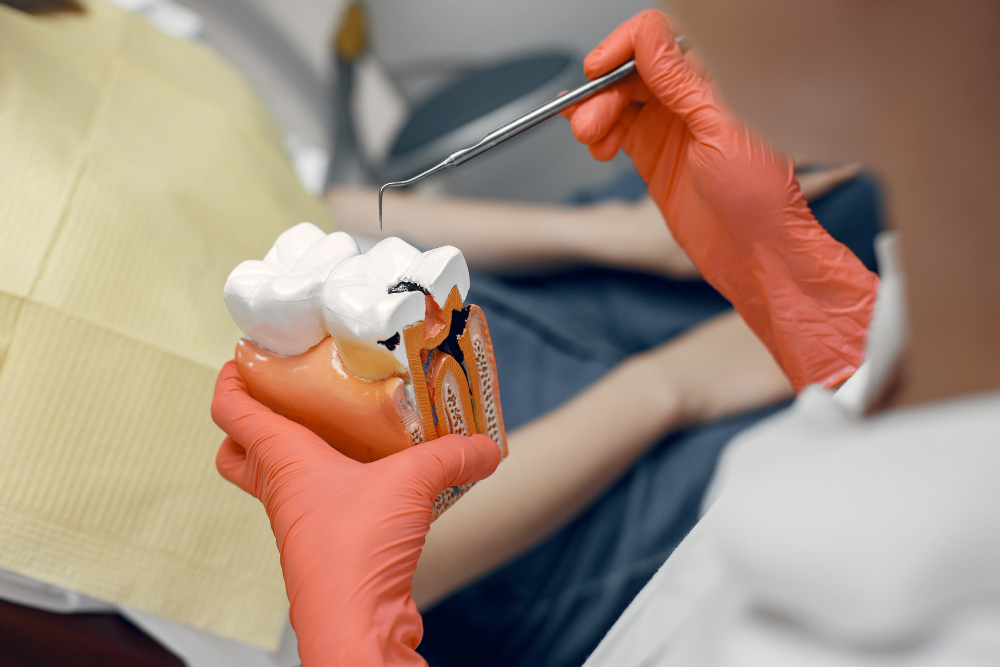
What does this decay pave way to?
Pain and discomfort is the initial depiction of a tooth decay as a child sometimes does not recognise the differentiation between sensitivity and pain. Further on it leads to an infective stage where there is probability for severe pain , swelling may or may not with pus discharge. A child is no longer able to chew food and it deteriorates his overall health.
How to prevent tooth decay?
There are some care that each parent should focus on. They are:
- Maintaining good oral hygiene habits (brushing, flossing, rinsing)
- Limiting sugary/acidic foods/drinks
- To encourage fluoride use (toothpaste, varnish, or supplements)
- Remember to schedule regular dental check-ups (every 6 months)
- To consider use of dental sealants for high-risk patients if advised by us.

Treatment
There is a comprehensive treatment plan for tooth decay in pediatric patients beginning with prevention and control.
Prevention and Control
- Oral Hygiene Instruction: Educating parents and patients on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
- Fluoride Therapy: Application of fluoride varnish or gel to teeth, especially for high-risk patients.
- Dietary Counseling: Advising on reducing sugary and acidic foods/drinks.
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule appointments every 6 months.
Non-Cavitated Lesions (early stages)*
The early stage is more of a preventive strategy which include:
- Fluoride Treatment: Apply fluoride varnish or gel to strengthen tooth enamel.
- Sealants:Place dental sealants on high-risk teeth (e.g., molars).
Cavitated Lesions (advanced stages)
This stage is of treatment phase which has to be carried out according to the progression.
-
Restorative Dentistry:
- Fillings (tooth-colored or stainless steel)
- Crowns (stainless steel or tooth-colored) -
Pulp Therapy:
- Pulpotomy (remove infected pulp)
- Pulpectomy (remove entire pulp)
- Extraction: Remove severely decayed teeth if necessary.
Follow-Up and Monitoring
Remember, early detection and prevention are key! This treatment plan should be tailored to each patient’s individual needs and circumstances.
Early detection and prevention are crucial!
Nursing Bottle Caries
Nursing bottle caries, also known as baby bottle tooth decay, is a common condition in infants and toddlers. It’s caused by the frequent and prolonged exposure of teeth to liquids containing sugar, like breast milk, formula, or juice, from a bottle or breastfeeding.
How to prevent such decay?
- Limit bottle usage to nap time and bedtime.
- Wean off the bottle by age 1.
- Use a pacifier or offer water after breastfeeding/ formula feeding.
- Clean teeth gently with a soft cloth or toothbrush.
- Schedule dental check-ups by age 1.
How do we recognize it is nursing bottle caries and not normal tooth decay?
This also shows visible signs of decay and they are on upper front teeth. There is discoloration or pitting. As it progresses it shows the symptoms as sensitivity or pain. It also causes difficulty in chewing and sleeping.
Treatments for such scenarios are
- Fluoride varnish or gel applications.
- Fillings or restorations.
- Pulp therapy (if necessary).
- Extraction (if severely decayed).
- Orthodontic evaluation (if needed).
What are the consequences which result ,if left untreated?
- Pain and discomfort.
- Infection or abscess.
- Difficulty eating or speaking.
- Malocclusion (misaligned teeth).
- Low self-esteem.
Fracture/ trauma
Fractures of teeth in pediatrics can be traumatic for children. It can happen during a fall or a fight in school or home. And the situation can be frightening both to children and parents. Not only do these accidents cause such traumas, but also severe tooth decay and biting onto hard objects can be a cause of it. It’s essential for parents to know in detail about the dental aspect of these traumas.
What types of fractures can occur to teeth?
This depends on extension or area where the fracture line is formed considering the anatomy of a tooth. The types are:
- Enamel fracture (chipping)
- Enamel-dentin fracture (smaller portion of tooth broken)
- Crown fracture (larger portion of tooth broken)
- Root fracture (tooth root broken
Symptoms of tooth fracture
- Pain or discomfort
- Sensitivity to temperature or sweets
- Visible crack or break
- Bleeding or swelling
Each symptom reveals itself according to the type of fracture that happened.
Treatment plan for the management :
As an initial step of management the child is assessed and detailed addressing of pain and swelling done. We may have to make use of radiographs (x-rays) to evaluate extent of fracture. Moving on further it’s important to rule out signs of infection or pulp damage and if needed further treatment protocol to be followed accordingly. The patient is made well assured about guidance on oral hygiene and diet to be followed for the days coming. So having said that moving on to the treatment protocols to be taken care of:
- Enamel fracture: Monitoring and maintaining good oral hygiene
- Enamel-dentin fracture: Restoring with a filling or bonding
- Crown fracture: Restoring with a filling, bonding, or crown
Root fracture: May require extraction or pulp therapy
How do we avoid the incidence of such tooth fractures?
- Encourage mouthguards during sports
- Teach children to avoid biting or chewing hard objects
- Maintain regular dental check-ups
- Promote good oral hygiene habits
Remember, prompt treatment and proper care can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications.
Malaligned Teeth
Malaligned teeth in children can be a concern for parents, but it’s essential to understand that it’s a common issue and can be addressed with proper orthodontic care. Consulting the best dentist for kids in Indiranagar at the right time ensures early intervention, which can prevent severe orthodontic issues in the future.
Causes of Malaligned Teeth in Children:
When to Consult an Orthodontist
- Around Age 7: Initial evaluation to identify potential issues.
- Noticeable Misalignment: If you notice significant crowding, spacing, or other alignment concerns.
Pediatric orthodontics is a specialized field of dentistry that focuses on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of dental and facial irregularities in children. It’s essential to address orthodontic issues early on to ensure proper oral development and prevent more severe problems from arising later in life.
Types of Pediatric Orthodontic Treatments:
- Preventive Orthodontics: Preventing problems through early intervention, such as correcting habits like thumb sucking or pacifier use.
- Interceptive Orthodontics: Addressing issues early, like crowding or spacing, to prevent more severe problems.
- Comprehensive Orthodontics: Full treatment plans for complex cases, often involving braces or other appliances.
Management of Pediatric Orthodontics:
- Early Evaluation: Initial assessments around age 7 to identify potential issues.
- Growth Monitoring: Regular check-ups to track development and adjust treatment plans.
- Phase I Treatment: Early intervention for specific issues, like expanding the palate.
- Phase II Treatment: Comprehensive treatment, often involving braces, after all permanent teeth have erupted.
Benefits of Paediatric Orthodontics:
- Improved Oral Function: Enhancing chewing, speaking, and overall oral health.
- Boosted Confidence: Straight teeth and a healthy smile can significantly impact self-esteem.
- Prevention of Future Issues: Addressing problems early on can prevent more severe complications.
- Optimal Timing: Treatment at the right stage of development can lead to more effective and efficient results.
- Enhanced Facial Aesthetics: Proper alignment and development can improve facial appearance.
Habits
What Parents need to Know
Oral habits in children can have significant impact on their oral health and overall development. Some habits lead to misalignment of teeth,, decay and other oral health issues.
Some of the common habits which affect oral health
- Thumb sucking
- Prolonged use of Pacifier
- Tongue Thrusting
- Teeth grinding
- Nail Biting.

How to break the habits?
- Gradual Weaning: Helping children gradually stop habits like thumb sucking or pacifier use.
- Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging good habits with praise and rewards.
- Distracting and Redirecting: Redirecting children’s attention away from unhealthy habits.
- Habit breaking appliance. Consult a pediatric dentist to help your child overcome the habit.
Our pediatric dentistry services are designed to meet the unique needs of children, from infancy through adolescence. By establishing good oral hygiene habits and addressing any dental issues early on, we can help set your child up for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
FAQs
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends a child's first dental visit by age 1 or within 6 months of their first tooth erupting.
Regular dental visits every 6 months, starting from the first visit.
Encourage good oral hygiene habits, limit sugary snacks, and ensure proper fluoride exposure.
Baby teeth help with chewing, speaking, and saving space for permanent teeth.
No, use a fluoride-free toothpaste for children under 3, and a pea-sized amount of regular toothpaste for children over 3.
Gradual exposure to dental visits, positive reinforcement, and gentle care from a pediatric dentist.
A specialized dentist with advanced training in treating infants, children, and adolescents.
Yes, we encourage parental involvement and support during appointments.
Appointments vary, but expect 30-60 minutes for routine visits.
Contact our office immediately for guidance and emergency care.