Management of Bleeding Gums and Gum Diseases
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are infections that affect the gums and supporting tissues surrounding the teeth. These start from gingivitis and can extend up to advanced periodontitis. For those experiencing persistent gum issues, treatments like bleeding gums treatment in Indiranagar and gum infection treatment in Indiranagar can help restore oral health effectively.
Stages of Gum disease
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Diseases
Most of us must have experienced an incidence of seeing blood in toothpaste. This is an evident symptom of gum disease, which is bleeding gums. The other symptoms include:
- Swollen or red gums
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
- Painful chewing
- Sensitive teeth
- Receding gums
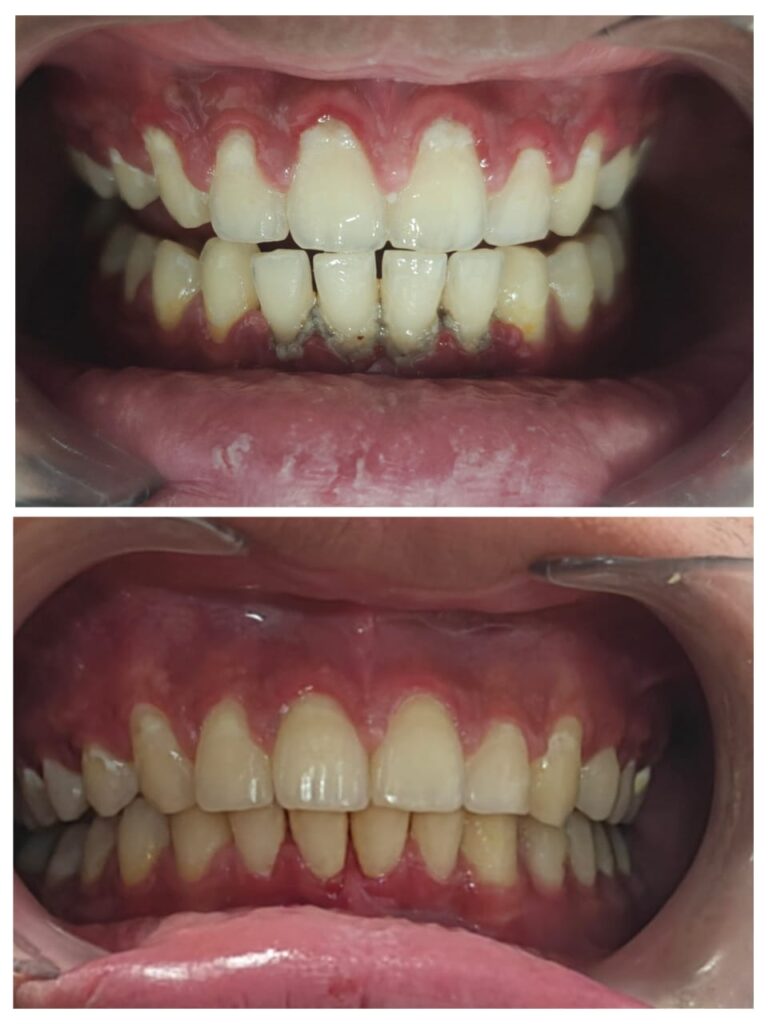
Stage 1: Gingivitis
This marks the initiation of gum diseases. Symptoms: Bleeding gums, redness, swelling Treatment:
- Professional cleaning (oral prophylaxis)
- Improved oral hygiene (brushing and flossing)
- Antibacterial mouthwashStage 2: Early Periodontitis
As gingivitis progresses to periodontitis the infection seeps in deep. Symptoms: Pocket formation (1-2 mm), bone loss, may have loose teeth Treatment:
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Antibiotics or antimicrobial therapy
- Improved oral hygieneStage 3: Moderate Periodontitis
Symptoms: Pocket formation (3-5 mm), bone loss, loose teeth Treatment:
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Bone grafting or tissue regeneration
- Antibiotics or antimicrobial therapy
- Occlusal adjustment (bite correction)Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis
Symptoms: Pocket formation (6 mm or deeper), significant bone loss, severe mobility of tooth. Treatment:
- Surgical intervention (flap surgery, bone grafting, or tissue regeneration)
- Extractions (if teeth are non-restorable)
- Dental implants or bridges (if teeth are missing)
- Occlusal adjustment (bite correction)
Treatment
Additional Treatments
– Laser therapy (LANAP or Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
– Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy
– Enzyme suppression therapy (to control inflammation)
Patients dealing with severe gum problems often benefit from specialized care such as bleeding gums treatment in Indiranagar, gum infection treatment in Indiranagar, or advanced options like laser gum treatment in Indiranagar for minimally invasive results.
How to prevent such conditions?
Regular dental checkups and cleaning have a huge impact on evaluation of gum health. Further on, brushing twice daily and flossing is the routine to be followed for maintaining oral hygiene and preventing such infections. Unhealthy habits like smoking have to be stopped. Moreover, managing systemic health conditions (e.g. Diabetes) should also be taken care periodically.
FAQs
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is an infection of the gums and bone that support the teeth.
Bleeding gums can be caused by gum disease, brushing too hard, or other factors like hormonal changes or vitamin deficiencies.
Symptoms include bleeding gums, swollen or red gums, bad breath, and loose teeth.
No, gum disease is not contagious, but poor oral hygiene and genetics can increase risk.
Diagnosis involves a dental exam, X-rays, and measuring pocket depth between teeth and gums.
Yes, treatment options include deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), antibiotics, and surgery.
Yes, prevention involves regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups.
Yes, research suggests links between gum disease and conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer's.
Yes, untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other complications.
Regular dental check-ups (every 6 months) can help prevent and detect gum disease early.
Blogs
- All Posts
- Gum Treatment